Kinetic Colon-on-a-plate®
Dynamic tracking of microbial and metabolic shifts from a small volume at high throughput
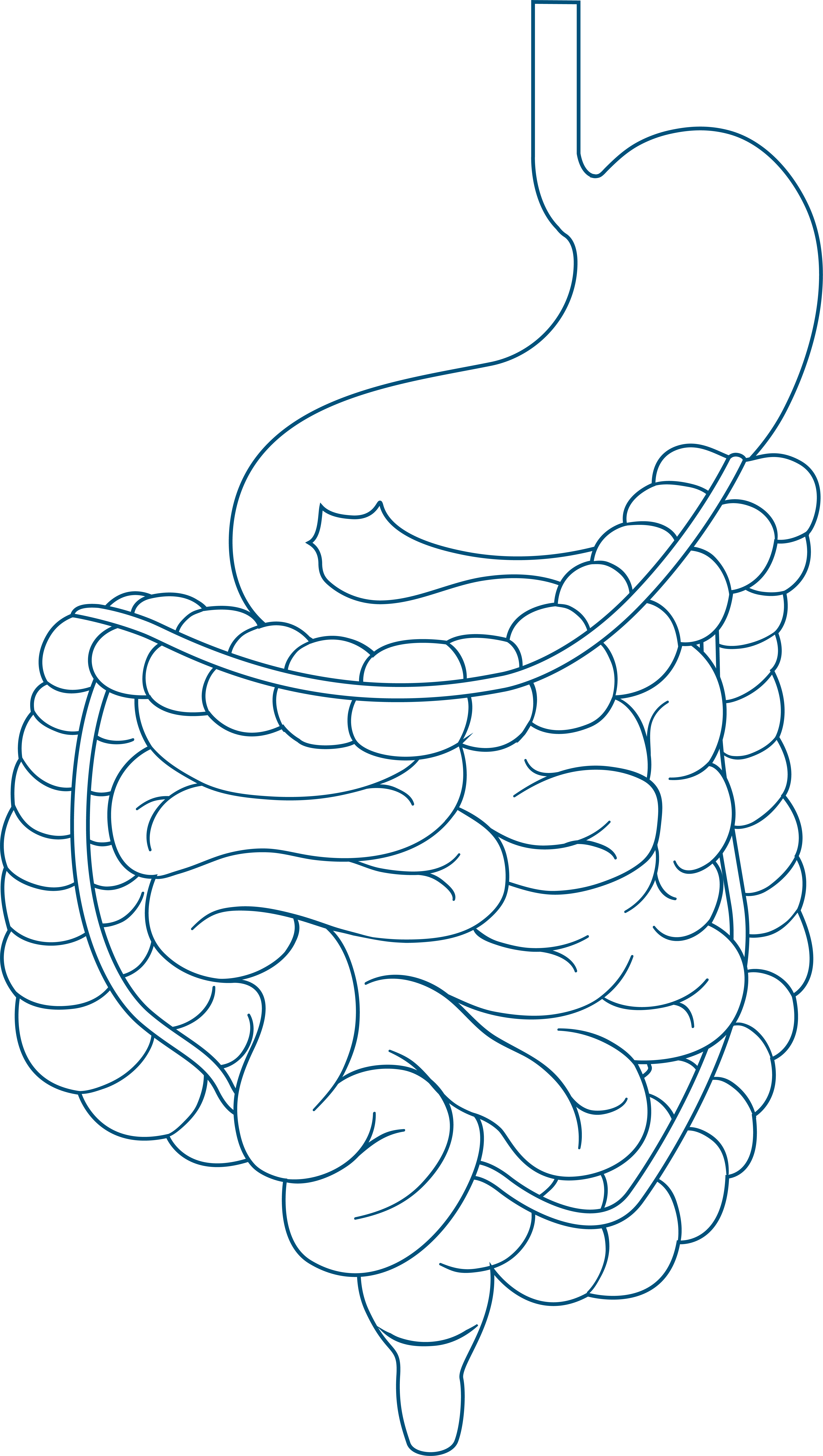
Microbial activity evolves as a function of time—metabolite concentrations rise and fall, and microbial communities shift. With the Kinetic Colon-on-a-plate®, you can track these dynamics in real-time, capturing key functional and compositional changes throughout a 48-hour fermentation window.
This controlled ex vivo model simulates the colonic microbiome with a single-dose setup and enables sampling at defined time points—typically 6, 24, and 48 hours. Despite working with small volumes, it generates high-throughput, time-resolved data, maximizing insight while minimizing material use and costs. It reveals not only the changes that occur but also the timing and mechanisms behind the microbiota's response to a compound.
This kinetic perspective enhances comparisons, strengthens mechanistic conclusions, and provides data that more accurately reflect biological processes.
The Kinetic Colon-on-a-plate® models both luminal and mucosal environments and can be adapted to various host profiles, including different age groups, health conditions, and microbiomes from multiple individuals. Like the original Colon-on-a-plate®, it can be paired with upstream pre-digestion models to simulate the full gastrointestinal journey, providing a comprehensive evaluation of compound behavior and microbiome interactions.
Run Once, Discover More
Unlike traditional systems that provide only a single endpoint readout, Kinetic Colon-on-a-plate® enables multiple samplings from the same reactor over key intervals, such as 6, 24, and 48 hours- all within a single experimental run in the same reactor.
This allows for tracking changes in the microbiome composition and its metabolic output as they happen, offering time-resolved insights into fermentation dynamics
Uncover Detailed Insights
Gain high-resolution datasets across a wide range of applications, including microbial composition, metabolic output, and fermentation kinetics. Capture robust, temporally distinct data at key intervals without interrupting the experiment. Track changes in SCFAs, lactate, pH, gas production, and microbiome composition, all from the same setup. This approach ensures consistency across time points, providing deeper insights into compound effects and microbial dynamics.
Optimize Sample Volume, Boost Throughput
By leveraging compact 10 mL reactors, the system strikes an ideal balance between flexibility and minimal sample volume, significantly reducing material costs and enhancing efficiency. This format supports high-throughput screening of multiple compounds or conditions, enabling detailed, longitudinal- nal analysis within a single experiment, helping to lower both sample and operational costs. compound effects and microbial dynamics.
How It Works
- Set Up the System
Combine your test product with donor-derived fecal microbiota and an optimized target-specific colonic medium in a 10 mL reactor.
- Replicate Colonic Conditions
Incubate the mixture at 37°C under anaerobic conditions for 48 hours to simulate the colonic environment. All variables (pH, oxygen, tempera ture) are tightly controlled.
- Collect Data at Key Time Points
Sample the reactor at 6, 24, and 48 hours to capture microbial and metabolic changes over time, providing dynamic insights into the fermentation process. You can also choose alternate sampling times as per your goals.
Why choose Kinetic Colon-on-a-plate®?
- Validate physiologically relevance with the option to add luminal and mucosal simulation.
- Accommodate various host types, including different age groups, health statuses, lifestyles, and variations.
- Perform multiple timepoint sampling to enable true kinetic analysis, offering deeper insights and higher resolution when comparing products.
- Integrate fully with the upper GI simulation for comprehensive analysis.
- Optimize sampling with a 10 mL volume to enhance reproducibility and reduce costs.
- Provide clear, actionable data to guide research, development, and regulatory strategies.