SHIME®
The SHIME®, model, a full gut simulation of colonic fermentation for preclinical or clinical studies supporting long-term microbiome interaction studies
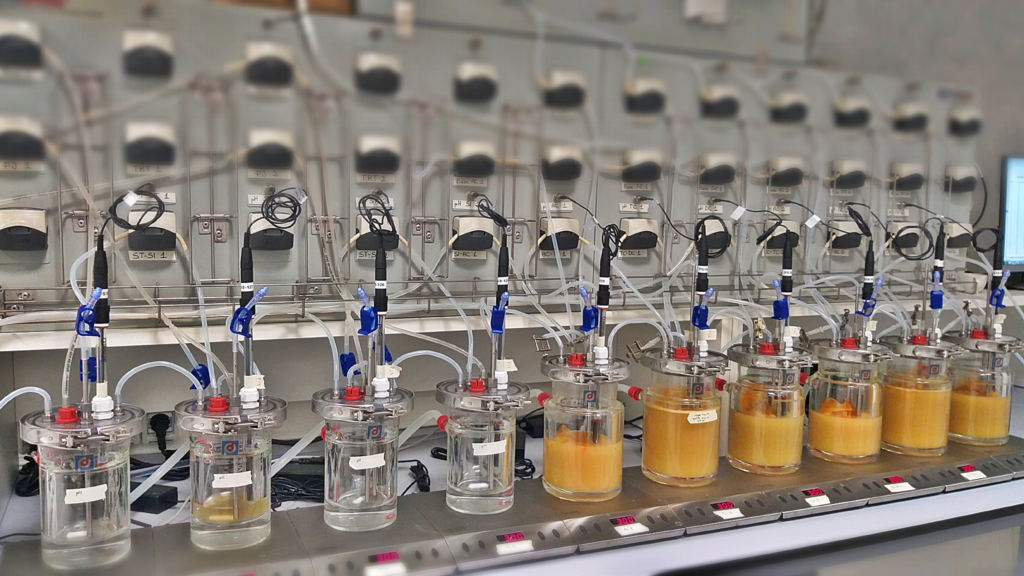

The SHIME® (Simulator of Human Intestinal Microbial Ecosystem) is currently the most representative in vitro technology for the combined simulation of the physiological, chemical, and microbiological properties of the gastrointestinal tract. The model enables the study of the impact of long-term repeated dosing and of the modulation of the microbiota in function of the gut location. The SHIME® can be seen as a clinical trial in vitro, which can provide the spatiotemporal insight into the mechanism of action of a specific treatment, therefore providing complementary data to in vivo studies.
The best in vitro colonic fermentation model for dynamic simulation the gastrointestinal tract
The SHIME® simulates all the compartments of the GI tract, starting with the stomach followed by the small intestine, the proximal and the distal colon (with an option to include the mouth and a specific ileal compartment with ileal microbial community). To be as close as possible to the in vivo situation, the SHIME® model reproduces multiple physiological and microbial in vivo parameters, including body temperature, intestinal volumes, enzyme concentrations, feeding cycles, pH, microbial diversity across anatomical compartments… Due to its flexibility, interindividual variability as well as various specific population groups (babies, children, elderly, healthy and diseased humans, or adjusted to the research question) and even animal models (cats, dogs and pigs) can easily be studied.
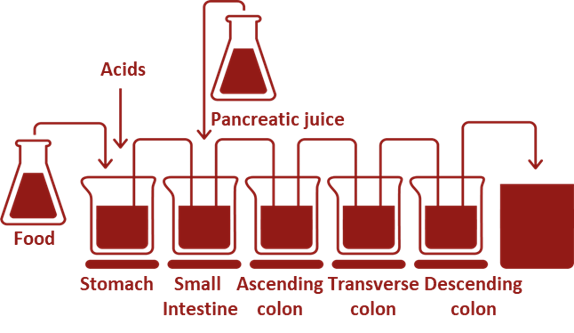
Difficult to study, but easy to simulate in the SHIME®: mucosal microbiome community, dysbiotic microbiome or pathogen infection
In addition to the physically separated proximal and distal colonic reactors, the SHIME® can be extended with the mucosal ‘compartment’ (M-SHIME®) simulating the microenvironment of the gut wall. This extension allows to study the specific roles of the mucosal and the luminal niches in the microbial community. Because of the differences in physiological conditions, these compartments are colonized by specific and differentiated microbial communities. This makes the SHIME® an excellent model to assess the localization of a treatment effect and its temporal onset following multiple daily doses.
To add to the versatility of the applications, the SHIME® technology can also be used to study the impact of repeated dosing on dysbiotic microbial communities for examples from IBD donors, or to study the infection cycle of pathogens.
Screening SHIME®
The Screening SHIME® has been developed to bridge the gap between the high throughput single-dose batch-type fermentations and the long-term repeated dosing SHIME®, the most detailed gut simulation.
As an adapted version of the SHIME® model, the Screening SHIME® is a fully automated – computer controlled simulation of the whole gastrointestinal tract. Utilizing a series of bioreactor vessels, it dynamically replicates the conditions of the stomach, small intestine, and colon. The test product is administered (daily) alongside one of the three daily feedings over an 8-day period. Thanks to its robust configuration, multiple colonic vessels can be simultaneously tested, facilitating the exploration of multiple test products and/or various colonic microbiomes.
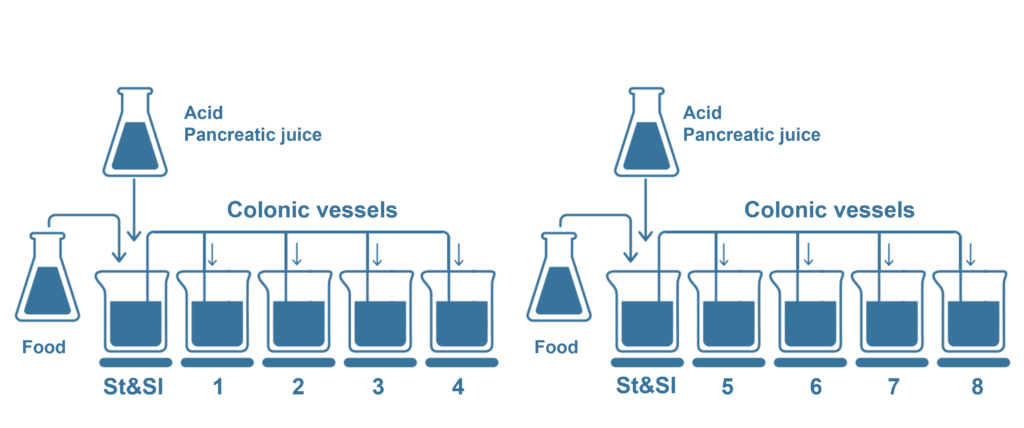
The Screening SHIME® combines throughput with the unique advantages of the SHIME®, including:
- Impact of repeated dosing of a test product on the microbiome
- Revealing long-term effects
- Offering kinetic insights in the onset and evolution of the effect and capturing changes over time
- Revealing the detailed mechanism of action
- Accounting for interindividual variability
- Assessment of the product’s effect on top of a normal diet
Additionally, the Screening SHIME® offers unparalleled advantages that position it as an exceptional screening tool for ex vivo colonic simulations, including:
- Mid-throughput, enabling the investigation of multiple colonic vessels in parallel
- Fast turnaround time
- Cost efficiency
- In vivo predictivity in only 8 days
Cindy Duysburgh, describe the Screening SHIME.
Microbial community composition and metabolomics analysis, gut permeability and intestinal immune responses: A full gastrointestinal in vitro analysis
The data that is generated during a SHIME® experiment sheds light on the interplay between test products and the human gut microbiota (microbial composition and activity). When coupled to off-line cell-based assays, the SHIME® can be used to generate data on the effect of a treatment at the level of the epithelial layer and immune parameters. Also the metabolomic profiles or specific metabolites can be screened by coupling the simulation to the in house MetaKey® platform.
Research endpoints
Microbial composition analysis
- qPCR panels and bespoken strain specific qPCR-detection (e.g. to quantify your LBP or probiotic)
- 16S rRNA gene profiling
- Shotgun Sequencing
- Flow cytometry
Microbial activity analysis
- SCFA, Lactate, Ammonium and pH
Metabolomics: MetaKey® platform
- LA-REIMS: General screening
- HPLC-HRMS: Targeted metabolite determination and specific panels
Host-interactions
- Bioavailability
- Barrier integrity and immuno-modulatory properties
- Tight junction proteins and mucin production
- Wound healing
- Adhesion/invasion of pathogens
Project-specific detections and analysis
Investigational topics